- Lift is a measure of the effectiveness of a predictive model calculated as the ratio between the results obtained with and without the predictive model.
- Cumulative gains and lift charts are visual aids for measuring model performance
- Both charts consist of a lift curve and a baseline
- The greater the area between the lift curve and the baseline, the better the model
Example Problem 1
A company wants to do a mail marketing campaign. It costs the company $1 for each item mailed. They have information on 100,000 customers. Create a cumulative gains and a lift chart from the following data.
- Overall Response Rate: If we assume we have no model other than the prediction of the overall response rate, then we can predict the number of positive responses as a fraction of the total customers contacted. Suppose the response rate is 20%. If all 100,000 customers are contacted we will receive around 20,000 positive responses.
| Cost ($) | Total Customers Contacted | Positive Responses |
| 100000 | 100000 | 20000 |
- Prediction of Response Model: A response model predicts who will respond to a marketing campaign. If we have a response model, we can make more detailed predictions. For example, we use the response model to assign a score to all 100,000 customers and predict the results of contacting only the top 10,000 customers, the top 20,000 customers, etc.
| Cost ($) | Total Customers Contacted | Positive Responses |
| 10000 | 10000 | 6000 |
| 20000 | 20000 | 10000 |
| 30000 | 30000 | 13000 |
| 40000 | 40000 | 15800 |
| 50000 | 50000 | 17000 |
| 60000 | 60000 | 18000 |
| 70000 | 70000 | 18800 |
| 80000 | 80000 | 19400 |
| 90000 | 90000 | 19800 |
| 100000 | 100000 | 20000 |
Cumulative Gains Chart:
- The y-axis shows the percentage of positive responses. This is a percentage of the total possible positive responses (20,000 as the overall response rate shows).
- The x-axis shows the percentage of customers contacted, which is a fraction of the 100,000 total customers.
- Baseline (overall response rate): If we contact X% of customers then we will receive X% of the total positive responses.
- Lift Curve: Using the predictions of the response model, calculate the percentage of positive responses for the percent of customers contacted and map these points to create the lift curve.
Lift Chart:
- Shows the actual lift.
- To plot the chart: Calculate the points on the lift curve by determining the ratio between the result predicted by our model and the result using no model.
- Example: For contacting 10% of customers, using no model we should get 10% of responders and using the given model we should get 30% of responders. The y-value of the lift curve at 10% is 30 / 10 = 3.
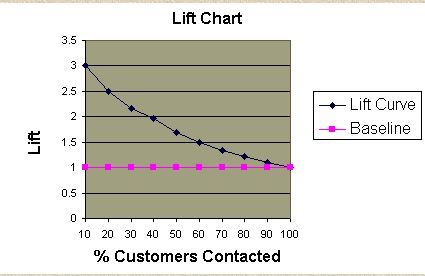
Analyzing the Charts: Cumulative gains and lift charts are a
graphical representation of the advantage of using a predictive model to
choose which customers to contact. The lift chart shows how much more likely
we are to receive respondents than if we contact a random sample of customers.
For example, by contacting only 10% of customers based on the predictive
model we will reach 3 times as many respondents as if we use no model.
Evaluating a Predictive Model
We can assess the value of a predictive model by using the model to score a set of customers and then contacting them in this order. The actual response rates are recorded for each cutoff point, such as the first 10% contacted, the first 20% contacted, etc. We create cumulative gains and lift charts using the actual response rates to see how much the predictive model would have helped in this situation. The information can be used to determine whether we should use this model or one similar to it in the future.
Example Problem 2
Using the response model P(x)=100-AGE(x) for customer xand the data table shown below, construct the cumulative gains and lift charts. Ties in ranking should be arbitrarily broken by assigning a higher rank to who appears first in the table.
| Customer Name | Height | Age | Actual Response |
| Alan | 70 | 39 | N |
| Bob | 72 | 21 | Y |
| Jessica | 65 | 25 | Y |
| Elizabeth | 62 | 30 | Y |
| Hilary | 67 | 19 | Y |
| Fred | 69 | 48 | N |
| Alex | 65 | 12 | Y |
| Margot | 63 | 51 | N |
| Sean | 71 | 65 | Y |
| Chris | 73 | 42 | N |
| Philip | 75 | 20 | Y |
| Catherine | 70 | 23 | N |
| Amy | 69 | 13 | N |
| Erin | 68 | 35 | Y |
| Trent | 72 | 55 | N |
| Preston | 68 | 25 | N |
| John | 64 | 76 | N |
| Nancy | 64 | 24 | Y |
| Kim | 72 | 31 | N |
| Laura | 62 | 29 | Y |
1. Calculate P(x) for each person x
2. Order the people according to rank P(x)
| Customer Name | P(x) | Actual Response |
| Alex | 88 | Y |
| Amy | 87 | N |
| Hilary | 81 | Y |
| Philip | 80 | Y |
| Bob | 79 | Y |
| Catherine | 77 | N |
| Nancy | 76 | Y |
| Jessica | 75 | Y |
| Preston | 75 | N |
| Laura | 71 | Y |
| Elizabeth | 70 | Y |
| Kim | 69 | N |
| Erin | 65 | Y |
| Alan | 61 | N |
| Chris | 58 | N |
| Fred | 52 | N |
| Margot | 49 | N |
| Trent | 45 | N |
| Sean | 35 | Y |
| John | 24 | N |
3. Calculate the percentage of total responses for each cutoff point
- Response Rate = Number of Responses / Total Number of Responses (10)
| Total Customers Contacted | Number of Responses | Response Rate |
| 2 | 1 | 10% |
| 4 | 3 | 30% |
| 6 | 4 | 40% |
| 8 | 6 | 60% |
| 10 | 7 | 70% |
| 12 | 8 | 80% |
| 14 | 9 | 90% |
| 16 | 9 | 90% |
| 18 | 9 | 90% |
| 20 | 10 | 100% |
4. Create the cumulative gains chart:
- The lift curve and the baseline have the same values for 10%-20% and 90%-100%.
5. Create the lift chart: