Topographic Maps
Elevation is added to a 2D map via contour lines
(see Fig. 6.7).
Contour line
= line connecting all points of the same elevation.
Contour Interval (abbreviated as C.I.) = the difference between two consecutive
contours.
Choice of contour interval depends on:
1) the level of detail needed
to be portrayed;
2) the scale of the map;
3) the range in elevation or relief of the area to be mapped.
Index Contour: as a general rule, every 5th contour, starting from sea
level, is an index contour. It is drawn as a heavy line and is labeled with
its elevation.
Gradient = change in elevation over
a specified horizontal distance.
On a contour map, gradient is determined along a line or stream course by:
1) using the contour lines to
determine the difference in elevation between two points;
2) using the horizontal scale to determine the distance between the
same two points;
3) dividing the vertical difference by the horizontal distance.
Elevation or Altitude = vertical distance between that point and a fixed datum
(usually mean average sea level), which by definition has an elevation of
zero.
Bench Mark:
a point whose elevation has been precisely defined by government surveyors.
Its location is marked by a small brass plate. Designated by “B.M.”
Spot Elevations: Marked with an
“X” or are shown at many section corners, bridges, road intersections, hilltops,
etc.
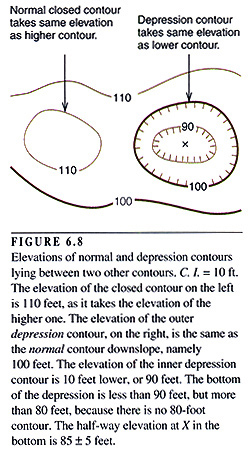
Depression Contours: closed contours with hachures (short lines perpendicular
to the contour line) pointing toward the lower elevations within a depression.
They generally encircle small depressions.