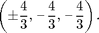Using Lagrange Multipliers to Solve a Constrained Max-Min Problem
Contents
Space probe
A space probe in the shape of the ellipsoid

enters the earth's atmosphere and its surface begins to heat. After 1 hour the temperature at the point (x,y,z) on the probe's surface is
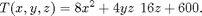
Find the hottest point on the probe's surface.
Step1 Write the constraint as g = 0. The function g is
syms x y z g = 4*x^2+y^2+4*z^2-16
g = 4*x^2 + y^2 + 4*z^2 - 16
Step 2 The extreme values of T on the probe's surface occur where the gradients of T and g are parallel. We set up the equations
T = 8*x^2+4*y*z-16*z+600
T = 8*x^2 - 16*z + 4*y*z + 600
gradg = jacobian(g,[x,y,z]) gradT = jacobian(T,[x,y,z])
gradg = [ 8*x, 2*y, 8*z] gradT = [ 16*x, 4*z, 4*y - 16]
We need to solve the equations
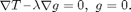
Step 3 We solve the equations.
syms lam
[lsol,xsol, ysol, zsol] = solve(gradT(1)-lam*gradg(1),gradT(2)-lam*gradg(2),gradT(3)-lam*gradg(3),g);
[xsol,ysol,zsol,lsol]
ans = [ 0, 4, 0, 0] [ 4/3, -4/3, -4/3, 2] [ -4/3, -4/3, -4/3, 2] [ 0, -2, 3^(1/2), -3^(1/2)] [ 0, -2, -3^(1/2), 3^(1/2)]
Step 4 Plug the resulting values for (x,y,z) into T and look to see where the maximum occurs. First we turn T into a function
Tfun = inline(vectorize(T)) double([xsol,ysol,zsol, Tfun(xsol,ysol,zsol)])
Tfun =
Inline function:
Tfun(x,y,z) = 8.*x.^2 - 16.*z + 4.*y.*z + 600
ans =
0 4.0000 0 600.0000
1.3333 -1.3333 -1.3333 642.6667
-1.3333 -1.3333 -1.3333 642.6667
0 -2.0000 1.7321 558.4308
0 -2.0000 -1.7321 641.5692
The hottest points on the probe's surface are