Fourier sine and cosine series
Contents
The cosine series of x
Let f(x) = x. First I calculate the Fourier cosine series of f on the interval [0,1].
syms x k n evalin(symengine,'assume(k,Type::Integer)'); f = x
f = x
The following commands compute the partial sum of the Fourier cosine series of f.
a = @(k) 2*int(x*cos(k*pi*x),x,0,1);
fourier_cosine_partial_sum = @(x,n) a(0)/2 + ...
symsum(a(k)*cos(k*pi*x),k,1,n);
Here are plots of the partial sums for n=2,5,10.
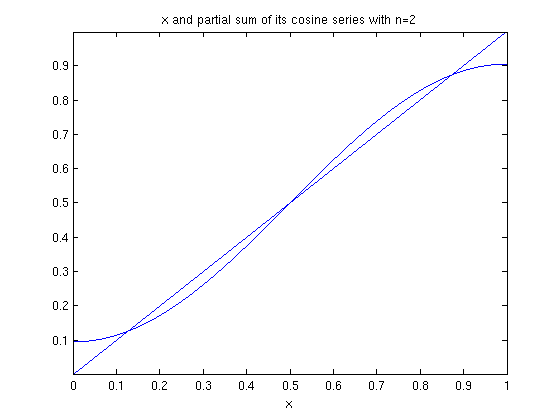
ezplot(f,0,1), hold on ezplot(fourier_cosine_partial_sum(x,2),0,1), hold off title('x and partial sum of its cosine series with n=2')
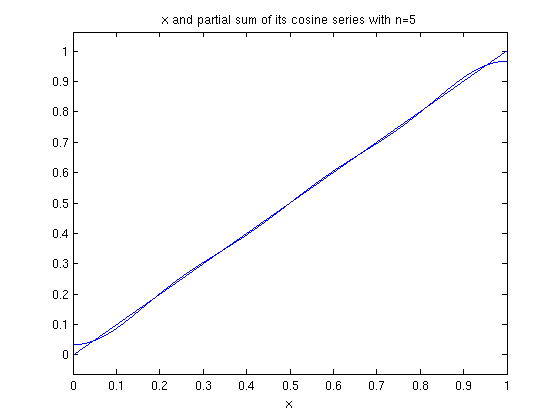
ezplot(f,0,1), hold on ezplot(fourier_cosine_partial_sum(x,5),0,1), hold off title('x and partial sum of its cosine series with n=5')
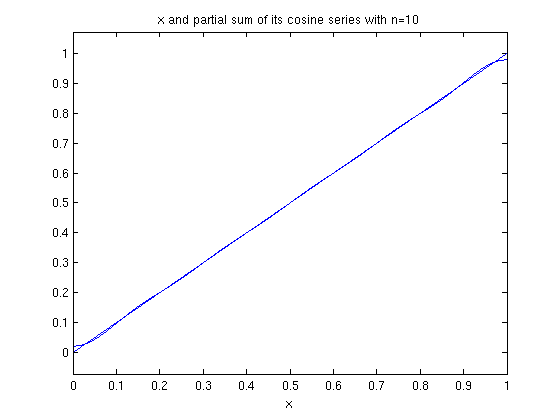
ezplot(f,0,1), hold on ezplot(fourier_cosine_partial_sum(x,10),0,1), hold off title('x and partial sum of its cosine series with n=10')
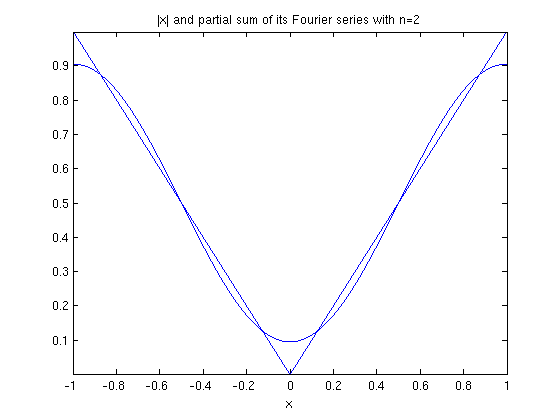
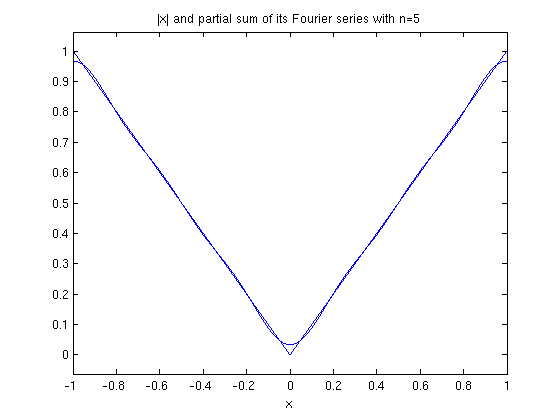
Recall that the cosine series is the Fourier series of the even extension of f. The even extension to [-1,1] is just abs(x). Here are plots of abs(x) and the Fourier cosine series of x on [-1,1].
ezplot(abs(x),-1,1), hold on ezplot(fourier_cosine_partial_sum(x,2),-1,1), hold off title('|x| and partial sum of its Fourier series with n=2')
ezplot(abs(x),-1,1), hold on ezplot(fourier_cosine_partial_sum(x,5),-1,1), hold off title('|x| and partial sum of its Fourier series with n=5')
The sine series of x
The following commands calculate the nth partial sum of the Fourier sine series of f.
b = @(k) 2*int(x*sin(k*pi*x),x,0,1); fourier_sine_partial_sum = @(x,n) symsum(b(k)*sin(k*pi*x),k,1,n);
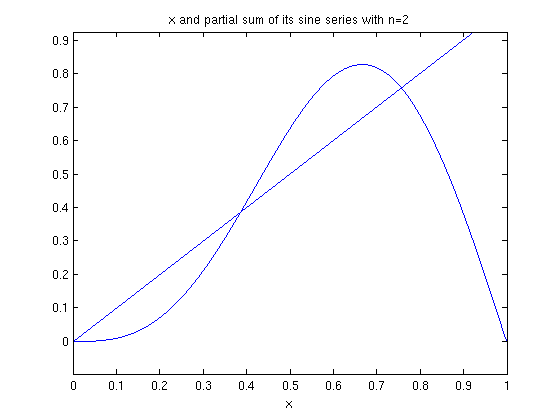
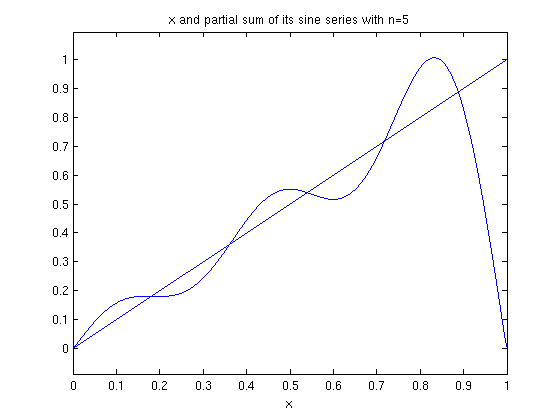
Here are plots of the partial sums for n = 2,5,10.
ezplot(f,0,1), hold on ezplot(fourier_sine_partial_sum(x,2),0,1), hold off title('x and partial sum of its sine series with n=2')
ezplot(f,0,1), hold on ezplot(fourier_sine_partial_sum(x,5),0,1), hold off title('x and partial sum of its sine series with n=5')
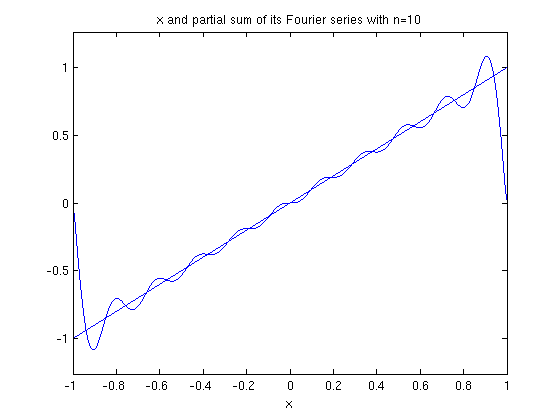
ezplot(f,0,1), hold on ezplot(fourier_sine_partial_sum(x,10),0,1), hold off title('x and partial sum of its sine series with n=10')
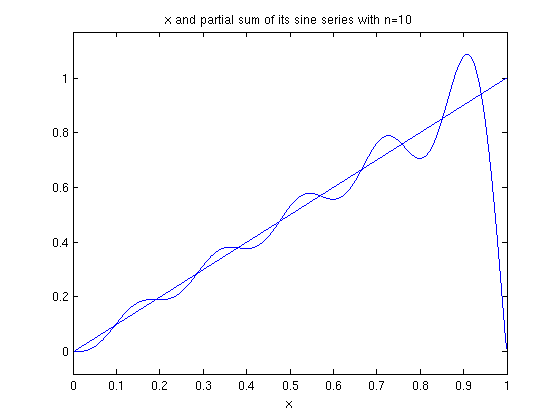
Recall that the Fourier sine series is the Fourier series of the odd extension of f. The odd extension of f to [-1,1] is x.
ezplot(x,-1,1), hold on ezplot(fourier_sine_partial_sum(x,10),-1,1), hold off title('x and partial sum of its Fourier series with n=10')