Lab 07: Bandwidth and Latency
The goal of this lab assignment to allow you to explore computer networking by measuring bandwidth and latency using off-the-shelf tools and with your own custom Python code. Additionally, you will play an educational game to review the topics discussed this week.
For this assignment, record your work in a Jupyter Notebook and upload it to the form below by 11:59 PM Friday, April 3.
Activity 0: Starter Notebook
To help you get started, we have provided you with a starter notebook, which you can download and then use to record your answers. To utilize the starter notebook, download it to wherever you are running Jupyter Notebook and then use the Jupyter Notebook interface to open the downloaded file.
The starter notebook is already formatted for all the various sections you need to fill out. Just look for the red instructions that indicates were you need to write text or the cyan comments that indicate where you need to write code.
Activity 1: SpeedTest
For the first activity, you are to measure the speed of various networking technologies by using the SpeedTest website. You are to use the following two connection types:
-
Wired or wireless connection from your laptop
-
Cellular connection from your phone (make sure you are using 4G/LTE and not WiFi)
To test the speed of each connection, simply go to the website on the
appropriate device: www.speedtest.net and hit the Go button. This will
measure your Ping, Download, and Upload speeds to generate a
result such as:


Note: For your phone, you may need to download and install an app. You can uninstall it after you are done testing the speed.
Speed Tests
Run the SpeedTest on each connection type a few times to get a representative sample and then complete the table below:
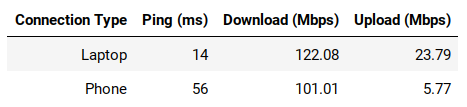
Analysis
After completing the table above with your speed tests, analyze the results by answering the following questions:
-
Which connection type had the best latency? Explain.
-
Which connection type had the best bandwidth? Explain.
-
What difference (if any) did you notice between download and upload speeds? Discuss why this could be.
-
Overall, which connection type was the best? Explain.
Activity 2: Bandwidth and Latency
For the second activity, you are to write two functions that you can
utilize to perform your own bandwidth and latency measurements.
The first is measure_bandwidth, which uses requests to download data
from a web server, while the second is measure_latency which uses a
low-level socket to connect to a remote server. For timing, we will use
Python's time module:
current_time = time.time()
Measure Bandwidth
The first function you need to complete is measure_bandwidth:
def measure_bandwidth(url):
''' Measure bandwidth by doing the following:
1. Record start time.
2. Download data specified by url.
3. Record end time.
4. Compute bandwidth:
bandwidth = (Amount of Data / Elapsed Time) / 2**20
'''
return 0
This function measures bandwidth by downloading the specified url using
the requests module and then computing the elapsed time using the time
module to record the start and stop times. Since we wish for the
measurements to be in terms of megabytes per second (MBps), we divide our
bandwidth by 2^20.
Once you have completed this function, you are to write a for loop that
measures the bandwidth of downloading each of the apps in the
URLS dictionary:
URLS = {
'Slack' : 'https://downloads.slack-edge.com/releases_x64/SlackSetup.exe',
'Zoom' : 'https://d11yldzmag5yn.cloudfront.net/prod/3.5.361976.0301/zoom_x86_64.tar.xz',
}
Your for loop should print output that looks like this:
Downloaded Slack with bandwidth of 40.85 MBps
Downloaded Zoom with bandwidth of 29.93 MBps
Hints
-
Record time using
time.time(). -
Use
requests.getto download data. -
To get the number of bytes we download we get check the length of the response objects
contentattribute. -
Note, we do not need to save anything to disk.
Measure Latency
The second function you need to complete is measure_latency:
def measure_latency(domain):
''' Measure latency by doing the following:
1. Create streaming internet socket.
2. Record start time.
3. Connect to specified domain at port 80.
4. Record end time.
5. Compute latency:
latency = Elapsed Time * 1000
'''
This function measures latency by connecting to the specified domain
using the socket module and then computing the elapsed time using the
time module to record the start and stop times. Since we wish for the
measurements to be in terms of milliseconds (ms) we multiply our latency by
1000.
Once you have completed this function, you are to write a for loop that
measures the latency of connecting to each of the servers in the DOMAINS list:
DOMAINS = [
'facebook.com',
'cnn.com',
'google.com',
'nd.edu',
'amazon.co.uk',
'baidu.com',
'europa.eu',
'yahoo.co.jp',
]
Your for loop should emit output that looks like this:
Connection to facebook.com has latency of 11.63 ms
Connection to cnn.com has latency of 9.15 ms
Connection to google.com has latency of 13.30 ms
Connection to nd.edu has latency of 29.24 ms
Connection to amazon.co.uk has latency of 126.67 ms
Connection to baidu.com has latency of 203.80 ms
Connection to europa.eu has latency of 117.01 ms
Connection to yahoo.co.jp has latency of 166.58 ms
Analysis
After writing the measure_bandwidth and measure_latency functions above
and testing them, answer the following questions:
-
Which applications had the best bandwidth? How do these bandwidth measurements compare to the ones you had in Activity 1? What explains the differences?
-
Which domains had the best latency? Which ones had the worst latency? What explains these differences?
Submission
Once you have completed your lab, submit your Jupyter Notebook using the form: