Reading 00: Unix Shell, Git
Readings
The readings for Friday, January 15 are:
-
The goal of this course is to get you familiar with the Unix programming environment. In particular, we will be spending almost all of our time in a Unix shell.
The first assignment is to read and work through Command Line Crash Course, which is a tutorial into using the command line interface on various operating systems (focus on the Unix shell).
Alternative, you may go through any of the following tutorials:
-
For this course, you will be using Git to keep track of your assignments and to submit your work.
The second assignment is to read and work through Pro Git, Chapters 1. Getting Started and 2. Git Basics.
Alternatively, you may go through any of the following tutorials:
Active Reading
To get the most out of your reading, you should be typing commands into a terminal and playing around with the things you reading.
Questions
Normally, you will have a couple of questions to answer for each reading. For this first assignment, however, you are to do the following:
-
Create a Bitbucket account if you don't have one already.
-
Fork the CSE-20189-SP16/assignments repository to create your own private repository.
Note: Keep the name of the repository assignments and the original permissions.
Access Controls
Please ensure that your repository is Private and that only CSE-20189-SP16 and your account have access to your repository.
To do this, as you go through forking process, make sure you check
This is a private repositoryandInherit repository user/group permissions.If you have already forked and forgot to mark these settings, you can fix your repository by doing the following:
-
Click on the
Settings(or Gear icon) link to go to the Settings page. -
Check the
This is a private repositorybox and save the settings. -
Next, click on the
Access Managementlink on the left. -
Finally, add the CSE-20189-SP16 account and give it Admin access.
Once you have done this then the repository is properly configured.
-
-
Clone your private repository to a machine such as your computer or one of the student machines.
SSH_ASKPASS workaround
If you try to do a
git cloneon the student machines and it starts but fails to ask you for a password, try running this command first:unsetenv SSH_ASKPASSThis will force
gitto use the terminal to ask you for your password rather than popup a window. -
Edit the
README.mdfile so that it has the appropriateNameandNetID. -
Commit your work.
Throughout this course, you will be using Git to submit your reading and homework assigments.
Commands
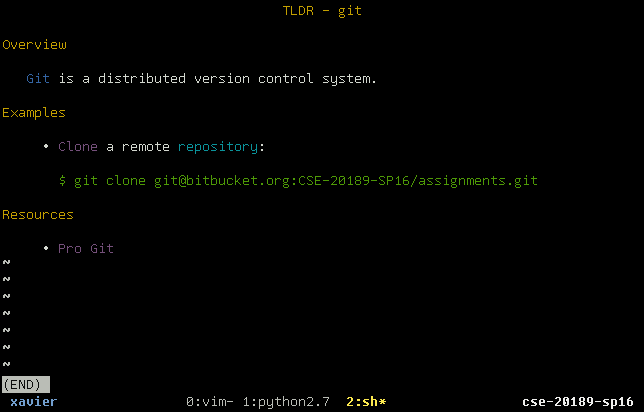
In addition to writing responses to any question prompts, each reading assignment will require you to create short summaries (tldr) of some of the commands we will be discussing for that week. Each command summary should provide a brief over of what the command does and then a succinct list of examples of commonly used applications of the command. Moreover, a list of resources or references may be provided at the bottom of the summary page for further information.
For instance the CSE-20189-SP16/assignments contains an example git.md
file in the reading00 folder. To view this file, you can use the
provided script:
$ ./mdview.sh reading00/git.md
This will process the Markdown flavored file and render it using elinks as shown below.
You can also use the tldr.sh script to search for commands in the current
directory :
$ ./tldr.sh git
This command will be useful once you have more summary pages and want to quickly grab the appropriate page for the corresponding command.
For this assignment, you are to modify the reading00/git.md summary page by
adding more example use cases (one example one is provided for you).
In addition to git, you should write at least two more summary pages for any of the following commands:
As with the git page, these additional pages should go in the reading00
folder and have the extension .md.
Note: The goal of these summary pages is to encourage you to build a set of notes and cheatsheets that will help you not only in this class, but in future endeavors as well. Because of this, you should record any examples that you find useful or interesting.
Markdown
The README.md and command summary files are annotated using Markdown.
This is a simple plain text formatting style that can be translated into
HTML.
For a more complete example of what you can do with Markdown, check out the
tutorial provided by Bitbucket. To view the result
of the translation, you can use the provided mdview.sh script.
Feedback
If you have any questions, comments, or concerns regarding the course, please provide your feedback at the end of your response.
Submission
To submit your response, please commit your work to the reading00 folder in
your Assignments Bitbucket repository.