Challenge 16: A-Mazing Paths
In addition to playing board games with his children, the instructor has also introduced them to the joy of solving mazes. This activity helps keep the children occuppied when the family is at a restaurant or on a long road trip.
Of course, the children have grown tired of this obvious ploy to occupy their time and want you to help them find the shortest path through a maze starting from a single position to any number of end positions.
To make things easier for you, they have taken mazes and encoded them in the format shown below:
Each cell in the maze can be one of the following values:
-
S: This is the starting cell. -
E: This is an ending cell. -
0: This is an open cell. -
1: This is a closed cell.
You can move through an open cell, but not a closed cell. From any
open cell, you can move horizontally, vertically, or diagonally to
another open or ending cell. Moving horizontally or vertically has
a cost of 1, while moving diagonally has a cost of 2.
Since their father is a cruel person and has given them many mazes of varying sizes, they will send you a series of mazes encoded in the format above. You are to use Dijkstra's Algorithm to compute the shortest path from the start point to any of the end points and output both the cost and the path itself.
Input
The input will be a series of mazes in the following format:
ROWS COLS
Cell0_0 Cell0_1...
Cell1_0 Cell1_1...
...That is, you will first be given two numbers, ROWS and COLS, which
correspond to the number of rows and columns in the maze. This is followed
by the CELLS in the maze where each line represents a row and the cells
in the row are separated by spaces. The number of ROWS and COLS will
be between 2 and 50 (inclusive).
The input will be terminated by two values of 0 for ROWS and COLS.
Example Input
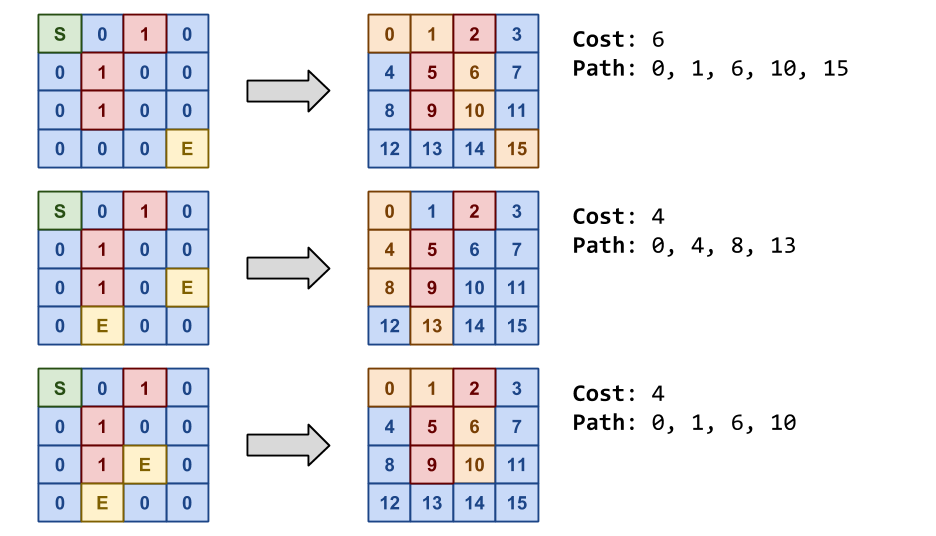
4 4
S 0 1 0
0 1 0 0
0 1 0 0
0 0 0 E
4 4
S 0 1 0
0 1 0 0
0 1 0 E
0 E 0 0
4 4
S 0 1 0
0 1 0 0
0 1 E 0
0 E 0 0
0 0Output
For each test case, output the cost of the shortest path from the starting cell to any of the ending cells and the cells in the shortest path.
Example Output
Cost: 6 Path: 0 1 6 10 15
Cost: 4 Path: 0 4 8 13
Cost: 4 Path: 0 1 6 10Note, as shown above, each cell is identified by a numerical ID based on its position in the maze:
Cell.Id = Cell.Row * Maze.Cols + Cell.ColumnThere should be spaces between each cell, but not after the last cell in the path.
If there are multiple paths with the same cost, choose the one where the path selects cells with lower numerical IDs from as shown in the third example.
Note, in the first example, we choose the path 0 1 6 10 15 instead of 0
1 6 7 11 15 because from the perspective of 15 node 10 has a lower
numerical ID than node 11.
If there are no possible paths from the starting cell to any of the ending cells, then output the following:
Cost: 0 Path: NoneSubmission
To submit your work, follow the same procedure you used for Reading 00:
$ cd path/to/cse-30872-fa19-assignments # Go to assignments repository
$ git checkout master # Make sure we are on master
$ git pull --rebase # Pull any changes from GitLab
$ git checkout -b challenge16 # Create and checkout challenge16 branch
$ $EDITOR challenge16/program.cpp # Edit your code
$ git add challenge16/program.cpp # Stage your changes
$ git commit -m "challenge16: done" # Commit your changes
$ git push -u origin challenge16 # Send changes to GitLabTo check your code, you can use the .scripts/submit.py script or curl:
$ .scripts/submit.py
Submitting challenge16 assignment ...
Submitting challenge16 code ...
Result Success
Score 6.00
Time 0.06
$ curl -F source=@challenge16/program.cpp https://dredd.h4x0r.space/code/cse-30872-fa19/challenge16
{"score": 6, "result": "Success"}Once you have commited your work and pushed it to GitLab, member to create a merge request. Refer to the Reading 08 TA List to determine your corresponding TA for the merge request.