Reading 00: Orientation, I/O
Everyone:
Welcome to CSE 30872 Programming Challenges, which (as the syllabus states) is a "course that revolves around solving brain-teaser and puzzle-type problems that often appear in programming contests, online challenges, and job interviews". What this means is that we will be studying common data structures, algorithms, and programming techniques that are useful in tackling a variety of problems.
Additionally, this semester we will also learn about different software development techniques such as debugging, testing, profiling, and packaging.
TL;DR¶
For this week, you should familiarize yourself with using Slack, setup your GitHub assignments repository, read about I/O and complexity, and then submit your responses to the Reading 00 Quiz.
Course Overview¶
Last semester, many of you took the Data Structures course where you learned about the properties and characteristics of different data structures (and perhaps you even implemented a few). The focus of this class, however, is not in the construction of these data structures, but rather their application. This means we will focus on when to use these data structures and algorithms and how to utilize them effectively rather than what they are. In concrete terms, we will not be implementing say a hash table; instead we will use one to solve a variety of problems.
Following the Hands-On Imperative, you will have the opportunity to put the material we discuss in class into practice via a respectful number of weekly programming challenges (two a week). Along with these challenges will be reading assignments to ensure you have a context or background knowledge for what we will be discussing in class. As with last semester in Systems Programming, the reading assignments will be automatically graded.
In fact all of your assignments will be automatically graded by dredd via the continuous integration system provided by GitHub. As you may have experienced during your internship this summer, testing is an important part of software engineering and we will therefore explore various aspects of software development including debugging, profiling, testing, packaging and more throughout the semester (if there is time).
Although each class will involve some amount of lecture, there will also be a lot of in-class activities and hands-on learning. Because of this, you are expected to come to class regularly and on-time.
Fortunately, however, there are no exams in this class. Instead, we
will have two in-class programming contests where you will get to work
in groups of 3 (similar to the ACM Programming Contest). Likewise, you
will also have to participate in two external programming contests such
as those provided by HackerRank or LeetCode.
Task 1: Slack¶
For communication outside of our meeting time, we will be using Slack,
specifically the #cse-30872-fa22 channel:
There is a class mailing list, but most day-to-day communication (including office hours and homework help) should take place on Slack.
Be aware of the following:
Task 2: GitHub¶
All of your work will be submitted to GitHub using git. Your third task is to setup your GitHub repository by doing the following:
-
Sign-in or create a GitHub account if you do not already have one.
-
Fork the class assignments repository from the following template:
This will create a private
cse-30872-fa22-assignments-$USERNAMErepository under your own account and linked to the nd-cse-30872-fa22 organization. -
Once this is done, you can clone your git repository to your local machine (or the student machines:
$ git clone git@github.com:nd-cse-30872-fa22/cse-30872-fa22-assignments-$USERNAME.gitNote, that GitHub has recently shutdown password authentication.To remotely access your repository from the command-line, you have two options:
-
Setup a Personal Access Token: With this method, GitHub will generate an application specific password that you can use with HTTPS. As the PAT is a long string of characters, it is recommended that you use it in conjunction with a password manager or keyring.
-
Setup SSH Keys: With this method, you generate a local public and private key pair on your computer and then upload the public key to GitHub. When accessing GitHub from the command-line, you will use the private key to authenticate to the server. This is the recommended way to setup your repository as it will allow for passwordless access.
Setup SSH Keys¶
Here is a quick tutorial on how to Setup SSH Keys on the student machines (if you have not already):
-
Generate SSH keys if you don't have them yet:
# Accept the defaults, don't make a password if you want to go passwordless $ ssh-keygen -
Copy the contents of
~/.ssh/id_rsa.pubto the SSH Keys section of your GitHub settings page:# Copy and paste the contents of this file into GitHub $ cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub -
Edit/create
~/.ssh/configto use this key with GitHub:# Add the following to your config (replace $NETID with your netid) $ $EDITOR ~/.ssh/config Host github.com User git Hostname github.com PreferredAuthentications publickey IdentityFile /escnfs/home/$NETID/.ssh/id_rsa
Once this is done, you should be able to do git operations without a password. You will need to accept the host key the first time by typing in "yes".
Note: Please update the
README.mdfile to include your name and NetID so it is straightforward to identify your account. -
GitHub Repository¶
You are responsible for ensuring that your GitHub assignments repository is in proper order, which means you have the correct settings and permissions set. Failure to properly configure your repository will adversely impact your grade.
Task 3: Reading¶
The readings for Wednesday, August 24 are
-
Competitive Programmer's Handbook
-
Chapter 1 Introduction
-
Chapter 2 Time Complexity
-
Note: Don't worry if you don't get the readings done by Monday, as this is the first week of class.
Task 4: Quiz¶
Once you have done the readings, answer the following Reading 00 Quiz questions:
To submit your answers, you will need create a answers.json or
answers.yaml file in the reading00 folder of your assignments
repository:
-
For this class, you must use a separate git branch for each assignment. This means that the work for each reading and challenge must be done in a separate branch. To create and checkout a new branch, you can do the following:
$ git checkout master # Make sure we are in master branch $ git pull --rebase # Make sure we are up-to-date with github repository $ git checkout -b reading00 # Create reading00 branch and check it outOnce you do the above, you should see the following output for the git-branch command:
$ git branch master * reading00The
*indicates that we are currently on thereading00branch. -
You can either hand-write the
answersfile using your favorite text editor or you can use the online form to generate the JSON data.A hand-written
answers.yamlmay look like the following:q1: [python,perl,ruby] q2: [n2,nf,nlogn,1,n,sqrtn,logn] q3: n q4: nThe equivalent
answers.jsongenerated using the online form may look like the following:{ "q1": [ "python", "perl", "ruby" ], "q2": [ "n2", "nf", "nlogn", "1", "n", "sqrtn", "logn" ], "q3": "n", "q4": "n" }You may use either format. To determine which symbols correspond to which response, take a look at the Reading 00 Quiz file.
To check your answers, you can use the provided
.scripts/check.pyscript:$ cd reading00 # Go into reading00 folder $ $EDITOR answers.json # Edit your answers.json file $ ../.scripts/check.py # Submit reading00 Checking reading00 quiz ... Q1 0.14 Q2 0.14 Q3 0.00 Q4 0.00 Q5 0.00 Score 0.29 / 3.00 Status FailureThis script will send your
reading00/answers.jsonfile to dredd, which is the automated grading system. dredd will take your answers and return to you a score as shown above. Each reading is worth 3.0 points.Note: You may check your quiz answers as many times as you want; dredd does not keep track of who checks what or how many times. It simply returns a score. -
Once you have your answers file, you need to add, commit the file, and push your commits to GitHub:
$ git add answers.json # Add answers.json to staging area $ git commit -m "Reading 00: Done" # Commit work $ git push -u origin reading00 # Push branch to GitHubNote: You may edit and commit changes to your branch as many times as you wish. Just make sure all of your work goes in the appropriate branch and then perform agit pushwhen you are done. -
When you are ready for your final submission, you need to create a pull request via the GitHub interface:
-
First, go to your repository's Branches page and then press the New pull request button for the appropriate branch:
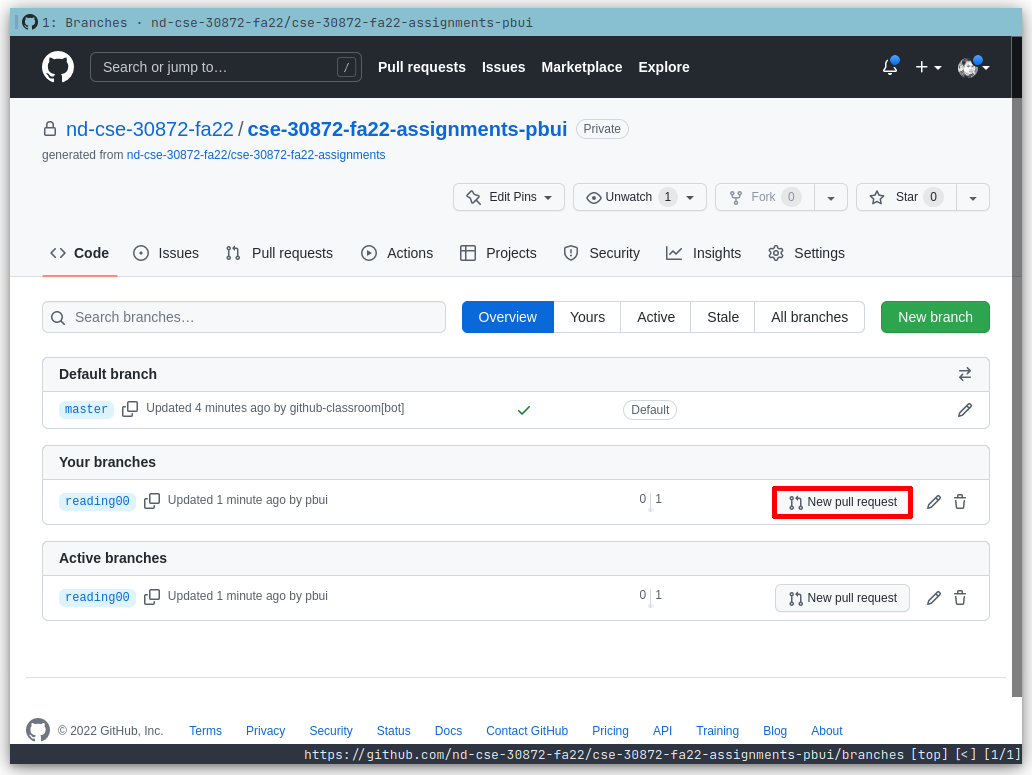
-
Next, edit the pull request title to "Reading 00", write a comment if necessary and then press the "Create pull request" button.
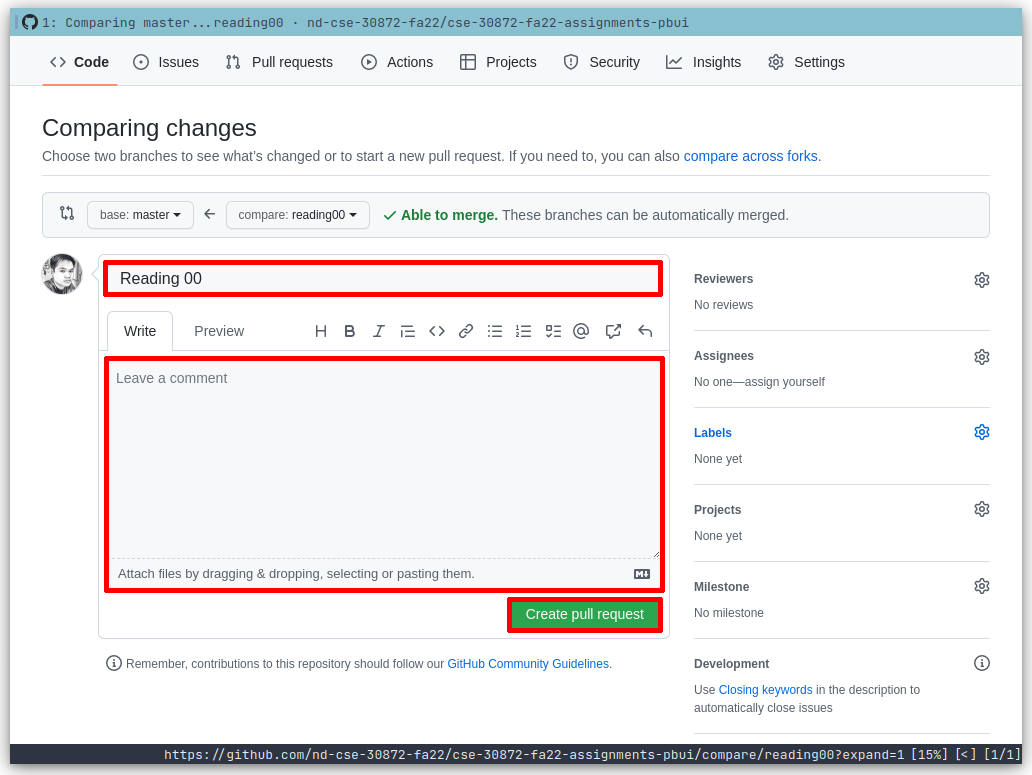
-
Finally, assign the pull request to the teaching assistant assigned to you for the given week and make sure all the checks have passed.
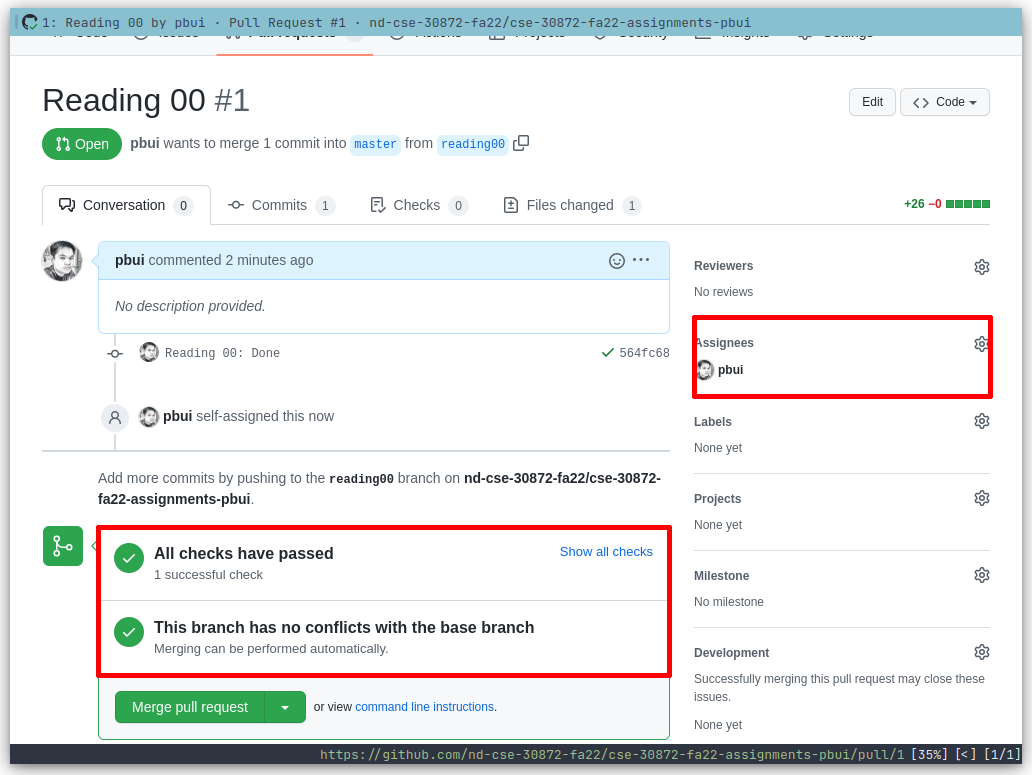
-
Every commit on GitHub will automatically check your quiz or code with dredd and the results of each run is displayed in the Checks tab of each commit as shown below:
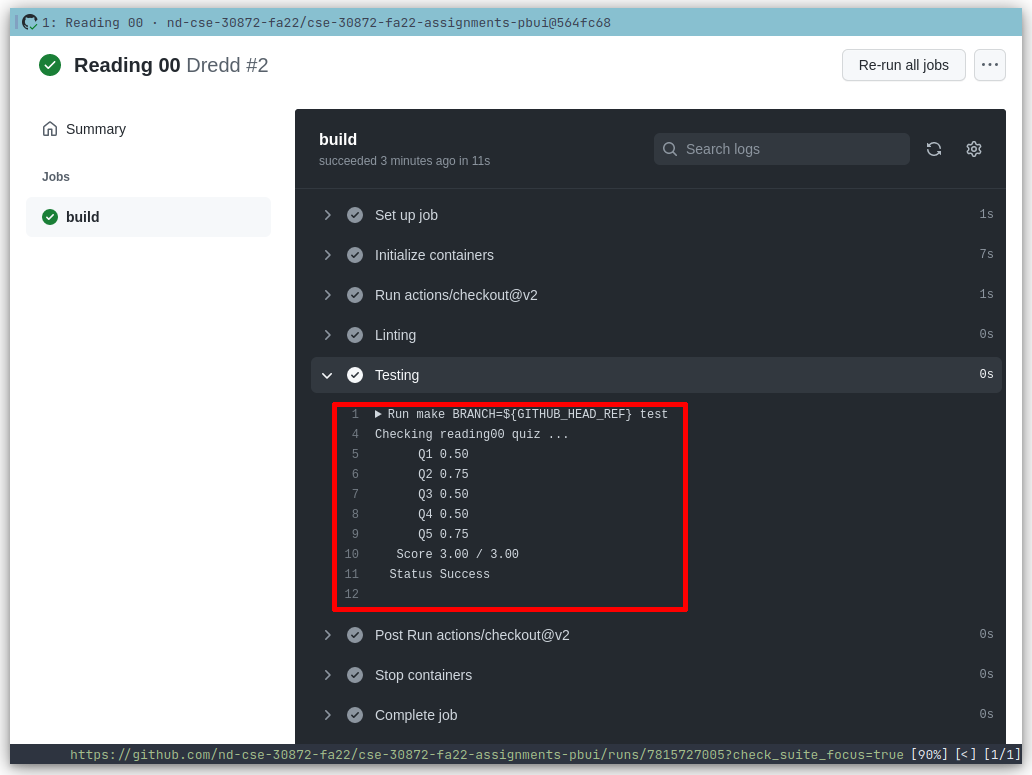
-
Graders¶
Please refer to the Reading 00 TA List to determine who your grader is for this week.
Once you have made the pull request, the instructor or teaching assistant can verify your work and provide feedback via the discussion form inside the pull request. If necessary, you can update your submission by simply committing and pushing to the appropriate branch; the pull request will automatically be updated to match your latest work.
When all work is graded, the grader will merge your branch and close the pull request.
Note: Please do not merge your own pull request. This makes it more difficult for the graders to keep track of what needs to be graded.
Qualitative Feedback¶
The purpose of this workflow is to provide you with better feedback. Instead of simply determining if your work is correct, the instructor will attempt to provide you with more qualitative feedback such as whether or not you used good programming practices or if your code could be improved or organized better.
The hope is that this will help you grow as programmers and develop some taste :).